What does DL mean?
Deep Learning is a subfield of machine learning that has revolutionized the way we approach artificial intelligence.
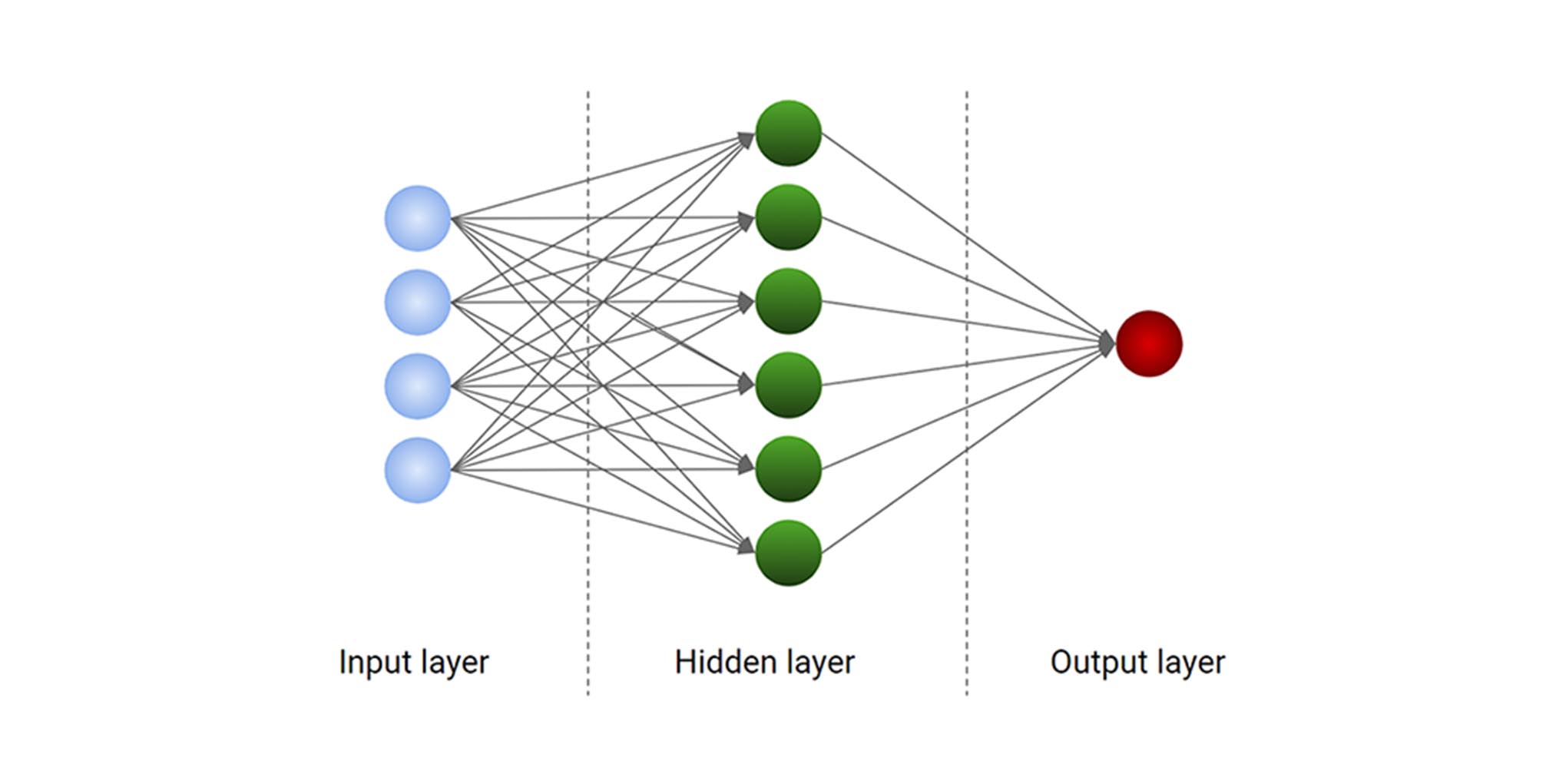
Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers to learn complex patterns in data. These neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain and are designed to recognize patterns and make decisions based on data.
Deep learning differs from typical machine learning models in terms of neural network design. Traditional models use basic networks with one or two computational layers.
While deep learning models have hundreds or thousands of layers. Unsupervised learning enables deep learning models to extract characteristics and refine outputs for increased precision- train the models
Key Characteristics
Artificial Neural Networks: Artificial neural networks, which consist of several interconnected layers of nodes, or “neurons,” are the foundation for deep learning models.
Distributed Representations: Deep learning models acquire the ability to depict data in a distributed manner, wherein every node within the network indicates a distinct feature or aspect of the data.
Hierarchical Representations: In order to represent data, deep learning models learn to work in a hierarchical manner, with early layers standing in for low-level features and later layers for high-level features.
Automatic Feature Learning: Rather than requiring human feature engineering, deep learning models can automatically extract pertinent features from raw data.

How does deep learning works?
Neural networks, also known as artificial neural networks, try to emulate the human brain by combining data inputs, weights, and bias, all of which serve as silicon neurons.
Deep neural networks are made up of numerous layers of interconnected nodes, each of which refines and optimizes the previous layer’s prediction or categorization. The input layer is where the deep learning model receives data for processing, while the output layer is where the final prediction or classification is formed- visible layers.
Backpropagation is a procedure that uses algorithms like gradient descent to compute errors in predictions before adjusting the weights and biases of the function by moving backwards through the layers to train the model. Forward propagation and backpropagation allow a neural network to make predictions and adjust for errors. The algorithm improves its accuracy over time.
A significant amount of processing power is needed for deep learning. Because they can do a lot of calculations on multiple cores and have a lot of memory available, high-performance GPUs are the best option. Cloud computing that is distributed may also be helpful.
For software requirements, most deep learning apps are coded with one of these learning open resource frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Keras..…

What’s your problem?
Our AI experts can help you design and automate your business.
Types of Deep Learning Models:
Different kinds of neural networks are used to deal with different issues or datasets.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Designed for image and video processing, CNNs use convolutional and pooling layers to extract features. Each node connects to another and has an associated weight and threshold. If the output of any individual node is above the specified threshold value, that node is activated, sending data to the next layer of the network.
Otherwise, no data is passed along to the next layer of the network. With each layer, the CNN increases in complexity, identifying greater portions of the image.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Designed for sequential data, RNNs use recurrent connections to capture temporal relationships. Use cases include stock market predictions or sales forecasting, or ordinal or temporal problems, such as language translation, natural language processing (NLP), speech recognition, and image captioning.
These functions are often incorporated into popular applications such as Siri, voice search, and Google Translate. They take information from prior inputs to influence the current input and output. While traditional deep neural networks assume that inputs and outputs are independent of each other, the output of RNNs depends on the prior elements within the sequence.
While future events would also be helpful in determining the output of a given sequence, unidirectional recurrent neural networks cannot account for these events in their predictions. An advantage over other neural network types is that RNNs use both binary data processing and memory. However, RNNs tend to run into two basic problems, known as exploding gradients and vanishing gradients.
When the gradient is vanishing and is too small, it continues to become smaller, updating the weight parameters until they become insignificant—that is, zero (0). When that occurs, the algorithm is no longer learning.
Exploding gradients occur when the gradient is too large, creating an unstable model. In this case, the model weights grow too large, and they will eventually be represented as NaN (not a number). One solution to these issues is to reduce the number of hidden layers within the neural network, eliminating some of the complexity in the RNN models.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Designed for generating new data samples, GANs consist of two neural networks that compete with each other. The “adversarial” part of the name comes from the back-and-forth between the two portions of the GAN: a generator and a discriminator.
The discriminator is the adversary, where the generative result (fake image) is compared against the real images in the dataset. The discriminator tries to distinguish between real and fake images, video, or audio. GANs train themselves. The generator creates fakes, while the discriminator learns to spot the differences between the generator’s fakes and the true examples.
When the discriminator is able to flag the fake, then the generator is penalized. The feedback loop continues until the generator succeeds in producing output that the discriminator cannot distinguish. The prime GAN benefit is creating realistic output that can be difficult to distinguish from the originals, which in turn may be used to further train machine learning models.
They are trained by using unlabeled data or with minor labeling. The potential disadvantage is that the generator and discriminator might go back-and-forth in competition for a long time, creating a large system drain. One training limitation is that a huge amount of input data might be required to obtain a satisfactory output.
Autoencoders: Designed for dimensionality reduction and generative modelling, autoencoders learn to compress and reconstruct data. Plain autoencoders were used for a variety of purposes, including reconstructing corrupted or blurry images. Encoders compress a dataset into a dense representation, arranging similar data points closer together in an abstract space.
Decoders sample from this space to create something new while preserving the dataset’s most important features. This also speeds transmission and reduces storage requirements. Autoencoders can be trained on unlabelled data, so they might be used where labelled data is not available. There are disadvantages to autoencoders.
The training of deep or intricate structures can be a drain on computational resources. And during unsupervised training, the model might overlook the needed properties and instead simply replicate the input data. Autoencoders might also overlook complex data linkages in structured data so that they do not correctly identify complex relationships.
For more articles:
—— > Where is Deep Learning used?
—— > Deep Learning architecture
—— > ML vs DL vs NN
—— > What is ML?
