How can we use AI for circular economy?
AI and Machine Learning applications can help enable and accelerate “circular” design and the adoption of circular economy business models in a variety of industries, including urban transportation, energy efficiency, and the agri-food industry.

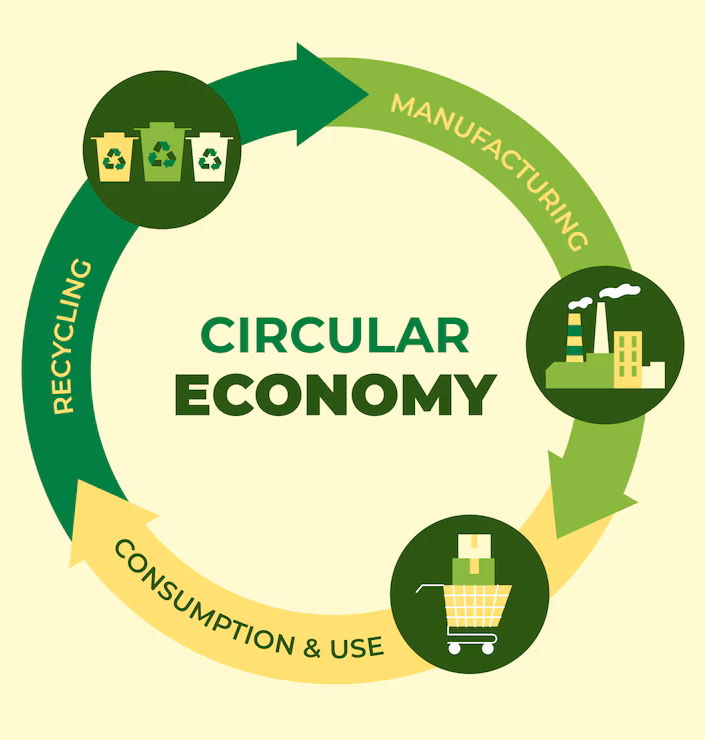
In a circular economy, resources never go to waste, and the environment is renewed. Products and resources are kept in circulation in a circular economy by recycling, composting, refurbishing, reusing, and maintaining. By severing the link between economic activity and the use of limited resources, the circular economy addresses issues such as pollution, waste, and biodiversity loss in addition to climate change.
Why do we need to move to a circular economy?
To protect the environment: Reusing and recycling products reduces natural resource use, biodiversity loss, and greenhouse gas emissions. The circular economy promotes efficient, sustainable products, reducing energy consumption and waste, and addressing excessive packaging design.
Reduce raw material dependence: Despite a growing population and increased need for raw resources, the circular economy provides a solution! By recycling and reusing materials, we can reduce the demand for new raw materials while also protecting those we already have.
Create jobs and save consumers money: Transitioning to a circular economy could boost competitiveness, stimulate innovation, and create jobs, with the EU aiming for 700,000 jobs by 2030.
How does it work?
In the transformation from the current linear economic model to the circular one, which aims to reduce resource waste by eliminating the concept of scrap in favor of a logic of reusing and recycling of already in use resources, new technologies, particularly AI, can promote and enable the adoption of circular economy business models.
In 2019, the Ellen MacArthur Foundation conducted research titled “Artificial Intelligence and the Circular Economy” to investigate the role of AI in the transition to a circular economy.
The study, which looked at the value chains of food and consumer electronics, showed how Artificial Intelligence may improve the circular design of products as well as the circular operation of business models and infrastructure.
According to the study’s findings, AI was already the most effective accelerator in 2019 for decoupling development from resource usage by restructuring production, consumption, and disposal systems in a circular way.
AI can revolutionize circular innovation in various sectors by interpreting complex data and providing clear feedback. It can accelerate the development of recyclable, biodegradable, or renewable products, components, and materials through machine learning-assisted iterative design processes.
AI can also accelerate the implementation of circular business models by facilitating the adoption of Product-as-a-Service or servitization and leasing models. By combining real-time and historical data, AI can increase product circulation and asset utilization, and improve reverse logistics infrastructure to close the loop on products and materials.
AIRAW (real-world project)
Problem: About waste electrical and electronic equipment seeks to reduce the environmental impacts of WEEE
Through various processes in most industries, such as maintenance, reuse, recycling, and composting, the circular economy aims to prevent waste and restore nature.
By setting targets to meet material demand in the EU, recycling has been identified as a key contributor to the security of raw material supply.
AIRAW demonstrates how such AI technology applied to multiple recycling applications can effectively benefit the entire EU recycling ecosystem.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are an essential component of electronic devices we use every day, such as computers, televisions, smartphones, and laptops. Manufacturing Electric and Electronic Equipment (EEE) requires a substantial amount of materials, including Critical Raw Materials (CRM).
AIRAW project aims at closing the technological gap of sorting and identifying CRMs from WEEE by introducing in the market an Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI) system that embeds a proprietary Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithm and therefore offers a new tool to increase the recycling percentage of CRMs and enhance the EU Circular Economy.
In particular, such technology will help industries recover a higher number of different materials efficiently and use CRMs.
The potential of AI in promoting a circular economy in agri-food, urban areas, energy efficiency, and sustainable mobility.
AI and digital technologies, combined with geolocalization, virtualisation, and de-materialisation, can enhance sustainability in urban contexts. These technologies optimize energy management, reduce consumption, and improve mobility by interpreting geospatial data and implementing real-time sharing models.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are crucial in agri-food, enabling sustainable circular economy models and optimizing processes throughout the supply chain. Real-time data collection, processing, and sales minimize waste generation, while AI models help reduce waste in consumption. These technologies provide entrepreneurs with a competitive advantage and contribute to sustainable development.

Supply chain sustainability
Do you select vendors with shared social values, minimize waste in manufacturing, and consider environmental impact in packaging and shipping decisions?
Supply chain sustainability involves incorporating environmental, social, and corporate governance considerations in raw material sourcing, product conversion, and delivery, supporting a circular economy.
Supply chain sustainability benefits people, profits, and the planet. Consumers, employees, and investors increasingly expect brands to address sustainability issues. A common language and data are essential for a net-zero future.
CEOs face challenges in achieving clear ROI and economic benefits, with 57% identifying CEOs as key to success. Sustainability can differentiate brands, align leadership with ESG goals, and increase revenue and profits by reducing waste and embracing lean principles.
Circularity promotes sustainability by reducing material usage, promoting repair and recycling, and aligning supply chains with values like reduce by design, repair, and reuse.
Supply chain leaders can drive near-term results by focusing on environmental sustainability. Four areas to explore include greener shipping, inventory positioning, packaging, and returns. Empower customers to make eco-friendly decisions, optimize inventory visibility, shift packaging to reflect changing buying patterns, and swiftly re-market returned products.
Supply chain leaders should focus on product planning and sustainable elements to achieve long-term goals. This includes using recycled materials, building a sustainable ecosystem of partners, rethinking packaging, adopting circular models, exploring new revenue models, adjusting packaging to reflect changing buying patterns, and swiftly re-marketing returned products to reduce waste and protect the bottom line.

Our sulotion for you
Using AI capabilities can help speed up return sorting, product re-merchandising, and repair lifecycle tracking, decreasing waste and environmental effect from returned items.
